The Moxy Mail Proxy
Moxy is a mail proxy that acts as a mail server for multiple
domains. Mail received for each domain is transparently proxied
to different hosts and/or ports.
With Moxy:
- User mail servers can transparently receive mail on non
standard ports (ie ports other than 25)
- Users who's MX record points to the Moxy host retain complete
control over their mail server configuration and may
continue to use the MTA of their choosing (Sendmail, Postfix,
Qmail etc.).
- The Moxy host can easily log mail bandwidth usage on a
per destination or per email address basis. Using
Moxy allows you to keep track of bandwidth used in a manner
that is independent of MTA and without having to parse eccentric
log files. Moxy includes tools like moxystats
and moxylogalyze that give you a real time
and complete view of mail bandwidth usage.
- A mail server can change IP instantly, without
needing to update the DNS MX record.
- Mail for a given domain can be directed to multiple
servers simultaneously.
- Users get anonymity: The location of destination
mail servers remain unknown to senders, all they see is
the host running Moxy.
- Moxy can be run on an existing mail server and proxy connections
for other domains without disrupting the current setup.
For many, there's a problem with the way email is routed
through the internet. If you are to receive mail, you are
expected to a have a mail server listening at a single (usually
static) IP, on port 25. This will (one day) be fixed by the
use of DNS SERV records but in the meantime Moxy solves the
problem and a few others.
Moxy has been released by Pat Deegan
and Psychogenic.com
under the terms and conditions of the GNU
GPL.
Requirements
The requirements for running Moxy are minimal, basically
all you need is a box with a Unix type TCP/IP stack (sockets
and all that) and GDBM support.
To be really usefull, Moxy needs to be run on a machine that
can receive connections on the standard mail port (25).
Finally, you need a few friends or clients with domains to
proxy mail for. Just set their MX record (in the DNS) to point
to the IP of the server you're running Moxy on and configure
Moxy to proxy mail for these domains.
How it works
Mail to Moxy host (MX for domains) is transparently proxied
to other hosts/ports:
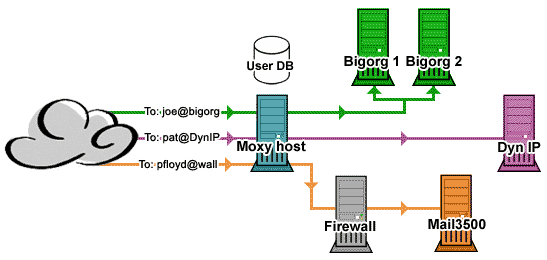
In the example above, the Moxy host acts as the MX record
for the Bigorg, DynIP and Wall domains. When mail arrives,
Moxy looks up the destination and determines the hosts and
ports to proxy the mail to. Moxy then opens a connection to
the destination(s), identifies the sender, requests to deliver
mail to the recipient(s) and sends the destinations' response
back to the sender. Mail data is then proxied from sender
to destination. Control over the validity of email addresses
etc remains in the hands of Bigorg, DynIP and Wall exclusively.
In the example, mail to users @Bigorg is sent to 2 different
hosts. Any number of host/port combinations may be assigned
as the destination for a given domain. Mail to users @Wall
is proxied to the Mail3500 machine on port 3500 thereby traversing
the firewall (with the sysadmin's approval of course).
Technical Summary
The developer section contains
the juicy details but here is a brief summary. Moxy runs as
a daemon listening for connections, usually on port 25 (configurable).
The daemon forks a process for incomming connections, which
handles the entire transaction with the sender.
Domain to host:port translations are accomplished using a
child of the DomainDB class (a specific instance class derived
from the DomainDB). This allows all sorts of databases to
be used, for now lookups are implemented for flat file or
gdbm DBs but it should be a simple matter to implement the
lookups from a relational DB (MySQL, PostgreSQL), an LDAP
directory or pretty much anything else.
Moxy minimizes the number of connections required to transmit
mail. If an MTA connects and declares its desire to send mail
to auser@domain1.com and another@other.net and if both these
domains resolve to the same destination, the connection will
be 'reused' and the message only sent once.
A similar scheme is used for logging as for domain lookups.
Log objects derived from the Log class currently implemented
include instances for logging to a text file, logging through
syslog and logging to a gdbm db. Again, it should be a simple
affair to create a new subclass to implement logging elsewhere
(to a MySQL table, for instance).
Please see the developer section
for more info and pretty pictures.
Setup
Using Moxy involves little more than editing the config file
and launching the program. For details, please see the page
on configuration.
|







